The tiny house movement has exploded into a 4.82billionglobalmarket,withindustryprojectionsshowingarobust4.24.82 billion global market, with industry projections showing a robust 4.2% compound annual growth rate through 2029 [1]. As traditional homeownership becomes increasingly unattainable for many Americans—with median home prices reaching 4.82billionglobalmarket,withindustryprojectionsshowingarobust4.2396,900 in January 2025—savvy buyers are turning to tiny houses as an affordable path to homeownership [2]. However, negotiating tiny house purchase like a pro requires a fundamentally different approach than traditional real estate transactions, as these unique properties present distinct challenges including depreciation concerns, financing complexities, and regulatory hurdles that can make or break your investment.
Table of Contents
Unlike conventional homes that typically appreciate over time, tiny houses on wheels depreciate similarly to recreational vehicles, losing an estimated 10,000to10,000 to 10,000to30,000 in value immediately after purchase [3]. This depreciation reality, combined with the fact that 73% of tiny house projects fail due to poor planning decisions, makes strategic negotiation absolutely critical for protecting your investment [4]. The tiny house market operates under different rules than traditional real estate, with unique factors such as RVIA certification, weight restrictions, and zoning compliance directly impacting both purchase price and long-term value retention.
This comprehensive guide reveals the insider strategies and professional techniques that successful tiny house buyers use to secure the best possible deals while avoiding costly mistakes. From leveraging market data and financing alternatives to navigating legal complexities and psychological negotiation tactics, you’ll discover how to approach every aspect of the tiny house purchase process with confidence and expertise. Whether you’re considering a custom-built tiny house on wheels, a pre-owned mobile unit, or a foundation-built small home, these proven negotiation strategies will help you save thousands of dollars while securing a tiny house that truly meets your needs and budget.
Understanding the Tiny House Market Landscape
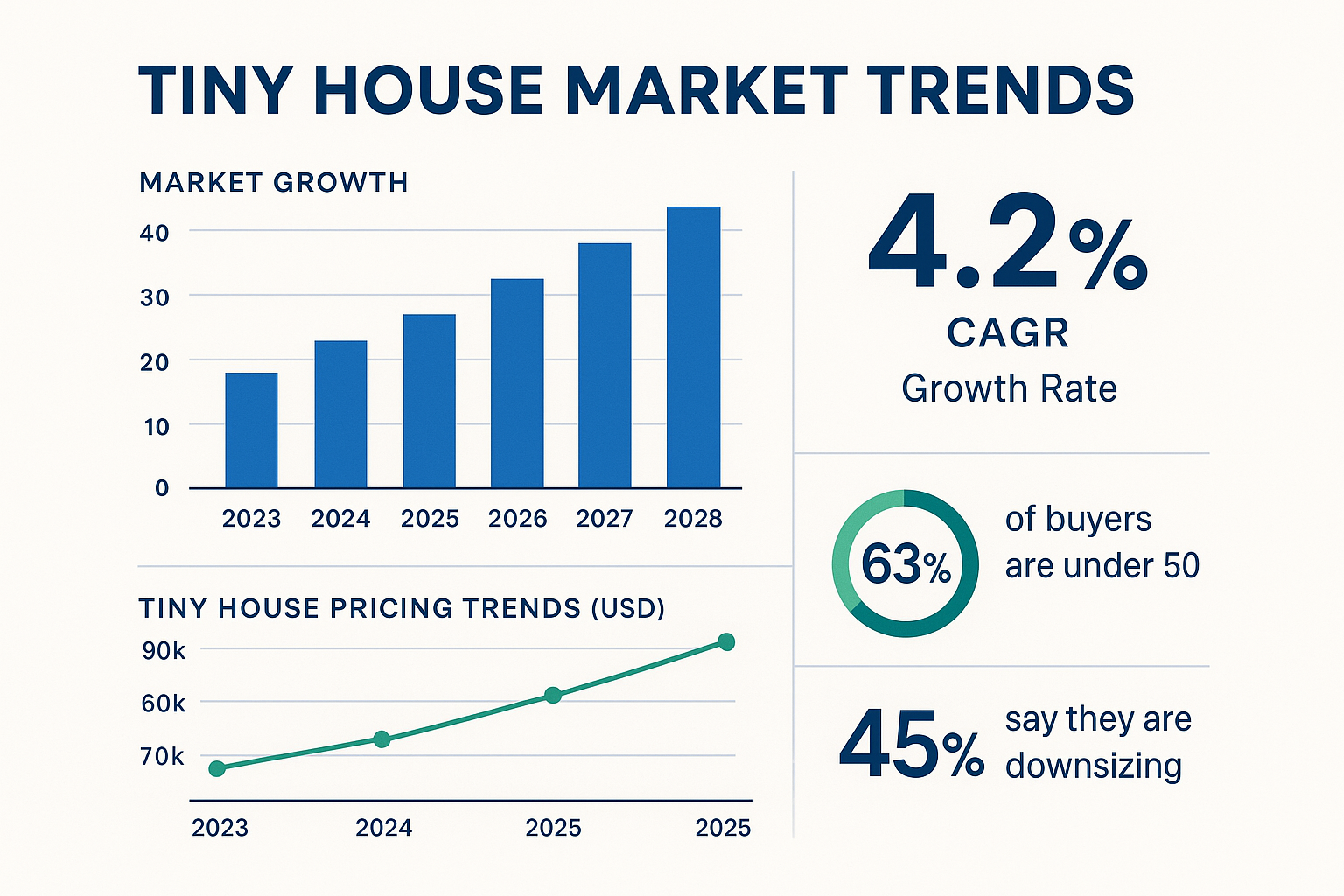
Current market trends and growth projections for the tiny house industry
The tiny house market in 2025 presents a complex landscape that savvy negotiators must understand to secure favorable deals. Recent market analysis reveals that the global tiny homes market reached $4.82 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 4.2% through 2029, driven primarily by affordability concerns and the growing appeal of minimalist living [5]. This growth trajectory creates both opportunities and challenges for prospective buyers, as increased demand can drive up prices while simultaneously expanding the available inventory of both new and used tiny houses.
Market segmentation plays a crucial role in negotiation strategy, with distinct pricing patterns emerging across different tiny house categories. Tiny houses on wheels (THOW) typically range from 35,000to35,000 to 35,000to110,000 for professionally built units, while foundation-built tiny homes command higher prices due to their permanent nature and potential for appreciation [6]. The used tiny house market presents particularly attractive negotiation opportunities, with depreciation rates of 3.5% annually creating significant price reductions for units just a few years old [7]. Understanding these depreciation patterns allows informed buyers to time their purchases strategically and negotiate from a position of market knowledge.
Regional variations significantly impact tiny house pricing and negotiation leverage. States with favorable tiny house regulations, such as Texas, Colorado, and North Carolina, tend to have more competitive markets with higher prices, while areas with restrictive zoning laws often present opportunities for below-market purchases [8]. The seasonal nature of tiny house sales also creates negotiation advantages, with winter months typically offering 10-15% lower prices as demand decreases and sellers become more motivated to close deals before spring [9].
The financing landscape directly influences negotiation dynamics, as traditional mortgage options remain limited for tiny houses. This financing gap creates opportunities for creative deal structures, including seller financing arrangements that can benefit both parties. Approximately 68% of tiny house owners purchase their homes without traditional mortgages, relying instead on personal savings, RV loans, or alternative financing methods [10]. This cash-heavy market gives well-prepared buyers significant negotiation leverage, particularly when dealing with sellers who need quick closings or have been struggling to find qualified buyers.
Current market trends indicate a shift toward higher-quality construction and premium features, with buyers increasingly willing to pay more for professionally built units with warranties and certifications. This trend creates a two-tiered market where certified builders command premium prices while DIY and uncertified builders face increased price pressure [11]. Understanding these quality distinctions allows negotiators to identify overpriced units and leverage construction quality issues during price discussions.
Pre-Negotiation Research and Preparation

Essential preparation steps before entering tiny house negotiations
Successful tiny house negotiations begin long before the first offer is made, requiring comprehensive research and preparation that goes far beyond traditional home buying due diligence. The unique nature of tiny house transactions demands specialized knowledge of construction standards, legal requirements, and market dynamics that can significantly impact both purchase price and long-term satisfaction. Professional negotiators understand that thorough preparation not only strengthens their bargaining position but also helps identify potential deal-breakers before emotional investment makes objective decision-making difficult.
Market research forms the foundation of effective negotiation strategy, requiring analysis of comparable sales data that accounts for the unique characteristics of tiny houses. Unlike traditional real estate, tiny house comparables must consider factors such as trailer quality, weight distribution, RVIA certification status, and mobility features that significantly impact value [12]. Successful buyers compile comprehensive databases of recent sales in their target price range, noting specific features, construction quality, and time on market to establish realistic price expectations and identify negotiation opportunities.
The research process should include detailed analysis of the specific builder or seller, as reputation and track record directly impact both initial pricing and negotiation flexibility. Established builders with strong warranties and customer satisfaction records typically maintain firmer pricing structures, while individual sellers or newer builders may offer more negotiation room [13]. Investigating the seller’s motivation through careful questioning and online research can reveal time pressures, financial constraints, or other factors that create negotiation leverage.
Documentation gathering represents a critical preparation phase that many buyers overlook, yet proper financial preparation can provide significant negotiation advantages. Pre-approval for financing, whether through traditional RV loans, personal loans, or alternative funding sources, demonstrates serious buyer intent and enables quick closing timelines that sellers often value highly [14]. Cash buyers enjoy the strongest negotiation position, but even financed purchases benefit from complete financial documentation that eliminates uncertainty during the negotiation process.
Inspection preparation requires specialized knowledge of tiny house construction standards and common problem areas that differ significantly from traditional homes. Understanding weight distribution issues, electrical system limitations, plumbing challenges, and structural concerns specific to mobile tiny houses enables buyers to identify potential negotiation points during property viewing [15]. Creating detailed inspection checklists that address tiny house-specific concerns helps ensure that no critical issues are overlooked during the evaluation process.
Legal research becomes particularly important for tiny house purchases due to the complex regulatory environment surrounding these alternative housing options. Understanding local zoning restrictions, parking regulations, and building code requirements in your intended location prevents costly surprises and provides negotiation leverage when sellers have unrealistic expectations about where their tiny house can be legally placed [16]. This research should include investigation of tiny house laws by state to ensure compliance with all applicable regulations.
The preparation phase should also include development of clear negotiation goals and limits, establishing both your maximum budget and minimum acceptable terms before emotional involvement clouds judgment. Successful negotiators create detailed wish lists that prioritize must-have features versus nice-to-have amenities, enabling strategic concessions during the negotiation process [17]. This preparation includes researching typical closing costs, transfer fees, and other transaction expenses that can add thousands of dollars to the final purchase price.
Essential Negotiation Strategies for Tiny House Purchases
Step-by-step flowchart of the tiny house negotiation process
The art of negotiating tiny house purchases requires a sophisticated understanding of both traditional real estate principles and the unique dynamics that govern alternative housing markets. Unlike conventional home negotiations where standardized processes and established market values provide clear frameworks, tiny house negotiations often involve custom-built properties, alternative financing arrangements, and regulatory complexities that demand flexible and creative approaches. Master negotiators recognize that successful tiny house deals require building rapport with sellers while maintaining firm boundaries around price, terms, and conditions that protect their long-term interests.
Price negotiation in the tiny house market begins with establishing a realistic baseline using comparable sales data, but must account for the significant variations in construction quality, materials, and features that can justify substantial price differences between seemingly similar units. Professional appraisers rarely handle tiny house valuations, leaving buyers to develop their own assessment methodologies based on cost per square foot, construction quality, and unique features [18]. Effective negotiators break down asking prices into component costs, analyzing the value of the trailer, structural materials, appliances, and labor to identify areas where prices may be inflated or where quality concerns justify price reductions.
The initial offer strategy requires careful calibration to demonstrate serious intent while leaving room for negotiation. Industry experts recommend starting offers at 85-90% of asking price for professionally built units in good condition, while used or DIY-built tiny houses may warrant initial offers of 70-80% of asking price depending on condition and market factors [19]. This approach respects the seller’s investment while acknowledging the depreciation realities and market dynamics that affect tiny house values.
Timing plays a crucial role in tiny house negotiations, with seasonal patterns and seller circumstances creating opportunities for strategic buyers. Winter months typically offer the best negotiation leverage as demand decreases and sellers face storage costs or seasonal access challenges [20]. Additionally, understanding the seller’s timeline and motivation can reveal opportunities for quick closings, flexible terms, or other concessions that provide mutual benefits while reducing the overall purchase price.
Inspection-based negotiations represent one of the most powerful tools in the tiny house buyer’s arsenal, as the complexity of mobile construction creates numerous opportunities for legitimate concerns that justify price adjustments. Common issues such as weight distribution problems, electrical code violations, plumbing leaks, or structural concerns can support requests for price reductions or seller-funded repairs [21]. However, successful negotiators approach inspection issues collaboratively, seeking solutions that address safety and functionality concerns while maintaining positive relationships with sellers.
Multiple offer situations require sophisticated strategies that go beyond simple price competition, as tiny house sellers often prioritize factors such as closing timeline, financing certainty, and buyer qualifications over the highest offer. Cash buyers can leverage their financing advantages by offering slightly lower prices with guaranteed quick closings, while financed buyers can strengthen their positions by providing comprehensive pre-approval documentation and flexible closing dates [22]. Creative offer structures, such as escalation clauses or rent-back agreements, can provide competitive advantages without necessarily increasing the base purchase price.
The negotiation of included items and exclusions often provides significant value opportunities in tiny house transactions, as these properties typically include custom-built furniture, specialized appliances, and unique storage solutions that would be expensive to replace. Successful negotiators create detailed lists of desired inclusions early in the process, using these items as negotiation tools that can offset price concessions or provide additional value without increasing the seller’s cash requirements [23]. Understanding which items are easily removable versus built-in features helps prioritize negotiation efforts on the most valuable inclusions.
Contract terms and conditions require special attention in tiny house negotiations due to the unique legal and practical considerations surrounding these alternative housing options. Standard real estate contracts often fail to address tiny house-specific issues such as trailer condition, weight certifications, RVIA compliance, and mobility requirements that can significantly impact the property’s value and usability [24]. Experienced negotiators insist on comprehensive inspections that include structural, electrical, and plumbing systems, as well as verification of legal compliance and roadworthiness for mobile units.
Financing and Payment Negotiation Tactics
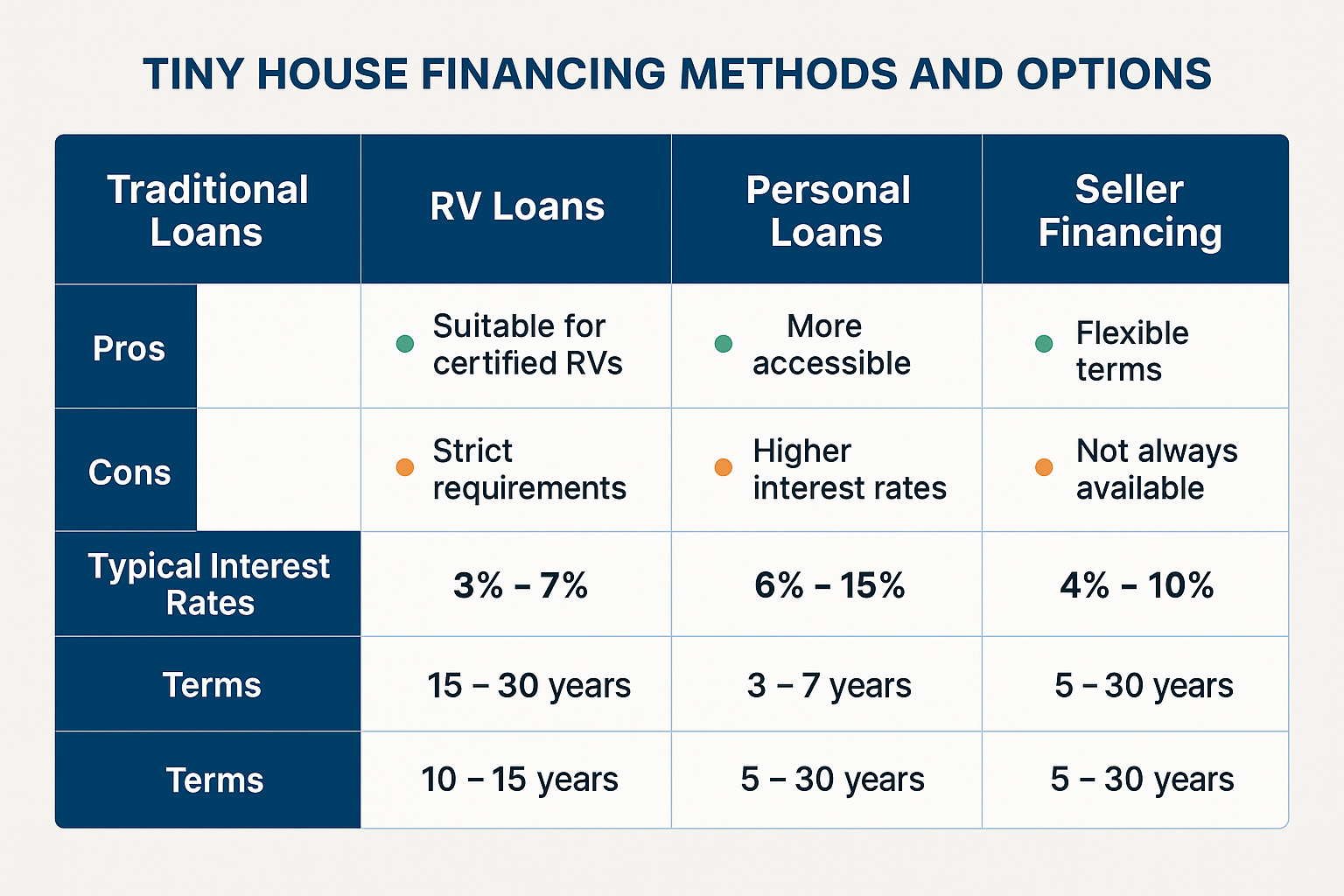
Comparison of different financing methods and their typical terms
The financing landscape for tiny houses presents both challenges and opportunities that skilled negotiators can leverage to secure better deals and more favorable terms. Unlike traditional mortgages that offer standardized rates and terms, tiny house financing requires creative approaches that often involve higher interest rates, shorter terms, and alternative lending sources [25]. However, this complexity also creates opportunities for innovative deal structures that can benefit both buyers and sellers while reducing overall transaction costs and risks.
Traditional mortgage financing remains largely unavailable for tiny houses on wheels, as most lenders classify these properties as recreational vehicles rather than real estate, eliminating access to conventional home loans with their favorable rates and terms [26]. This financing gap has created a market opportunity for alternative lenders, credit unions, and specialized tiny house financing companies that offer products specifically designed for this market segment. Understanding the full range of available financing options enables negotiators to structure deals that work within these constraints while minimizing costs and maximizing flexibility.
RV loans represent the most common financing option for tiny houses on wheels, typically offering terms of 10-15 years with interest rates ranging from 3% to 7% depending on credit scores and loan amounts [27]. These loans require that the tiny house meet RVIA certification standards or similar construction requirements, which can become a negotiation point when dealing with non-certified units. Buyers can leverage financing requirements during negotiations by requesting seller concessions for certification costs or by using financing limitations to justify lower offers on non-compliant units.
Personal loans provide another financing avenue, though typically with higher interest rates of 6% to 15% and shorter terms of 3-7 years [28]. The higher monthly payments associated with personal loans can limit buying power, but the faster payoff schedule appeals to buyers seeking to minimize long-term debt obligations. Negotiators can use personal loan limitations as leverage for price reductions, particularly when dealing with sellers who need quick closings and may be willing to accept lower prices for guaranteed financing.
Seller financing arrangements offer perhaps the greatest opportunity for creative negotiation, as they eliminate traditional lending requirements while providing benefits for both parties. Sellers can achieve higher effective sale prices through interest earnings while avoiding immediate tax consequences of large capital gains, while buyers can access financing that might otherwise be unavailable [29]. Successful seller financing negotiations typically involve interest rates between 4% and 10%, with terms ranging from 5 to 30 years depending on the seller’s financial needs and risk tolerance.
The negotiation of seller financing terms requires careful attention to both parties’ needs and constraints, with successful deals often involving graduated payment schedules, balloon payments, or other creative structures that address cash flow concerns. Buyers should propose terms that provide sellers with reasonable returns while maintaining affordable monthly payments, often suggesting interest rates slightly above current savings account yields but below traditional lending rates [30]. Security arrangements, such as retaining title until full payment or requiring comprehensive insurance coverage, help address seller concerns while enabling favorable financing terms.
Cash purchases provide the strongest negotiation position in the tiny house market, as they eliminate financing contingencies and enable quick closings that sellers often value highly. Cash buyers can typically negotiate 5-10% discounts off asking prices in exchange for fast, guaranteed closings, particularly when dealing with motivated sellers facing time pressures or carrying costs [31]. However, even cash buyers should consider the opportunity costs of tying up large amounts of capital in depreciating assets, potentially negotiating for seller financing even when cash is available.
Down payment negotiations can significantly impact both the purchase price and overall deal structure, particularly in seller-financed transactions where traditional lending requirements don’t apply. While RV loans typically require 10-20% down payments, seller financing arrangements can be structured with minimal down payments in exchange for higher interest rates or other concessions [32]. Buyers should consider the trade-offs between larger down payments that reduce monthly obligations and smaller down payments that preserve cash for other investments or emergency reserves.
Payment timing and structure negotiations can provide additional value beyond simple price reductions, particularly for sellers with specific cash flow needs or tax planning objectives. Offering to accelerate payments, provide seasonal payment schedules, or structure payments around the seller’s other income sources can justify price concessions while meeting both parties’ financial objectives [33]. These creative payment arrangements often prove more valuable to sellers than simple price increases, creating win-win scenarios that strengthen the overall negotiation relationship.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
The legal landscape surrounding tiny house purchases presents complex challenges that can significantly impact both negotiation strategies and long-term ownership satisfaction. Unlike traditional real estate transactions governed by well-established legal frameworks, tiny house purchases often involve navigating ambiguous regulations, varying local ordinances, and evolving legal precedents that require careful attention during the negotiation process [34]. Understanding these legal complexities enables buyers to identify potential issues early, negotiate appropriate protections, and avoid costly surprises that could undermine their investment.
Title and registration issues represent one of the most critical legal considerations in tiny house negotiations, as the classification of these properties varies significantly between jurisdictions and can affect everything from financing options to insurance coverage. Tiny houses on wheels typically require vehicle registration and may need to comply with Department of Transportation regulations for road travel, while foundation-built tiny houses may be subject to traditional real estate title requirements [35]. Negotiators must verify that sellers can provide clear title and proper registration documentation, as issues in these areas can prevent legal ownership transfer and create significant liability concerns.
The complexity of tiny house titling becomes particularly important when dealing with custom-built units or properties that have been modified since original construction. Many DIY builders fail to properly document their construction process or obtain necessary permits, creating title clouds that can complicate future sales or financing [36]. Experienced negotiators insist on comprehensive documentation of the construction process, including permits, inspections, and compliance certifications that demonstrate legal construction and support clear title transfer.
Zoning and parking regulations present ongoing legal challenges that directly impact tiny house usability and value, making these considerations essential elements of the negotiation process. Most traditional zoning codes do not specifically address tiny houses, leaving property owners to navigate complex interpretations of existing regulations that may classify these structures as accessory dwelling units, recreational vehicles, or non-conforming structures [37]. Before finalizing any purchase, buyers should verify that their intended parking location allows tiny house placement and use, as violations can result in fines, forced relocation, or legal action that significantly impacts the property’s value.
The regulatory environment varies dramatically between states and local jurisdictions, with some areas embracing tiny house development while others maintain restrictive policies that limit placement options. Understanding tiny house laws by state becomes crucial for buyers who may need to relocate their tiny house or who want to understand their long-term options for property placement. This knowledge also provides negotiation leverage when dealing with sellers who may have unrealistic expectations about where their tiny house can be legally placed.
Building code compliance represents another critical legal consideration that can significantly impact both safety and resale value. While tiny houses on wheels often fall outside traditional building code requirements, many jurisdictions are developing specific tiny house codes that address safety, structural, and habitability concerns [38]. Buyers should verify that their prospective purchase meets applicable building codes and safety standards, as non-compliant structures may face forced modifications, occupancy restrictions, or complete prohibition in certain areas.
Insurance requirements and availability create additional legal complexities that must be addressed during the negotiation process. Traditional homeowner’s insurance typically does not cover tiny houses on wheels, requiring specialized RV or mobile home insurance that may offer different coverage levels and exclusions [39]. Understanding insurance requirements and costs helps buyers budget accurately and negotiate appropriate protections, such as seller warranties or insurance transition periods that provide coverage during the ownership transfer process.
Contract law considerations become particularly important in tiny house transactions due to the unique nature of these properties and the frequent use of custom contracts rather than standardized real estate forms. Standard purchase agreements may not address tiny house-specific issues such as trailer condition, weight certifications, mobility requirements, or compliance with various regulations [40]. Successful negotiators insist on comprehensive contracts that clearly define all aspects of the transaction, including inspection rights, compliance warranties, and remedies for discovered defects or legal issues.
The enforcement of contracts and warranties presents additional challenges in the tiny house market, as the mobile nature of these properties can complicate legal proceedings and make it difficult to pursue remedies for contract breaches or construction defects. Buyers should negotiate clear jurisdiction clauses, dispute resolution procedures, and enforcement mechanisms that provide practical remedies for potential problems [41]. This includes consideration of where legal proceedings would take place, which state’s laws would apply, and how judgments could be enforced against mobile property that might be moved to different jurisdictions.
Common Negotiation Mistakes to Avoid

Common negotiation errors and their solutions for tiny house purchases
The unique nature of tiny house transactions creates numerous opportunities for costly mistakes that can undermine even the most well-intentioned negotiations. Unlike traditional real estate purchases where established processes and professional oversight help prevent major errors, tiny house negotiations often involve direct buyer-seller interactions, custom contracts, and specialized knowledge requirements that increase the risk of significant oversights [42]. Understanding these common pitfalls enables buyers to avoid expensive mistakes while maintaining productive negotiation relationships that lead to successful transactions.
Emotional decision-making represents perhaps the most dangerous trap in tiny house negotiations, as the appeal of minimalist living and the uniqueness of individual properties can cloud objective judgment about value, condition, and suitability. The tiny house community’s emphasis on lifestyle and values can create emotional connections that override practical considerations such as construction quality, legal compliance, or financial prudence [43]. Successful negotiators maintain emotional distance during the evaluation and negotiation process, relying on objective criteria and predetermined limits to guide their decisions rather than allowing enthusiasm to justify poor financial choices.
The tendency to fall in love with a specific property before completing due diligence creates negotiation weakness that experienced sellers can exploit. Buyers who become emotionally invested in particular tiny houses lose their ability to walk away from unfavorable terms, eliminating their most powerful negotiation tool [44]. Professional negotiators recommend viewing multiple properties and maintaining active interest in several options throughout the negotiation process, preserving the psychological freedom to reject unreasonable terms or excessive prices.
Inadequate research and preparation frequently lead to negotiation failures, as buyers who lack comprehensive market knowledge find themselves unable to justify their positions or identify reasonable compromise solutions. The complexity of tiny house construction, regulations, and market dynamics requires extensive preparation that goes far beyond traditional home buying research [45]. Buyers who attempt to negotiate without understanding comparable sales data, construction costs, regulatory requirements, and financing options inevitably find themselves at significant disadvantages when facing knowledgeable sellers or builders.
The failure to obtain professional inspections represents a critical mistake that can result in expensive surprises after purchase completion. Many buyers assume that tiny houses are simple enough to evaluate without professional assistance, overlooking complex systems, structural issues, or code violations that require specialized expertise to identify [46]. The relatively low cost of professional inspections compared to potential repair costs makes this false economy particularly dangerous, as hidden problems can easily exceed the entire purchase price of the tiny house.
Unrealistic price expectations based on incomplete market analysis or wishful thinking frequently derail negotiations before they can reach productive compromise solutions. Some buyers base their expectations on DIY construction costs without accounting for professional labor, permits, warranties, and other factors that justify higher prices for completed units [47]. Conversely, other buyers accept inflated asking prices without researching comparable sales or understanding depreciation patterns that should inform their negotiation strategies.
Poor timing decisions can significantly impact negotiation outcomes, as buyers who rush into purchases without adequate preparation or who delay decisions beyond reasonable market timeframes often find themselves with limited options and reduced leverage. The seasonal nature of tiny house sales creates predictable patterns that informed buyers can exploit, while uninformed buyers may find themselves competing in peak markets or dealing with limited inventory during high-demand periods [48]. Understanding these timing dynamics enables strategic buyers to optimize their negotiation positions while avoiding unnecessary pressure or competition.
The failure to establish clear negotiation limits and priorities before beginning discussions frequently leads to confusion, inconsistent positions, and missed opportunities for mutually beneficial agreements. Buyers who enter negotiations without predetermined maximum prices, minimum acceptable terms, and clear priorities often find themselves making reactive decisions that fail to serve their long-term interests [49]. Successful negotiators develop comprehensive negotiation plans that include multiple scenarios, fallback positions, and clear decision criteria that guide their responses to various seller proposals.
Inadequate attention to contract details and legal protections creates long-term risks that may not become apparent until after the transaction is complete. The complexity of tiny house ownership, including ongoing regulatory compliance, maintenance requirements, and potential relocation needs, requires comprehensive contract provisions that protect buyers’ interests throughout the ownership period [50]. Buyers who focus exclusively on purchase price while neglecting warranty terms, inspection rights, and legal protections often discover expensive problems that could have been addressed through more thorough contract negotiations.
Communication failures and relationship management mistakes can transform potentially successful negotiations into adversarial conflicts that prevent mutually beneficial outcomes. The personal nature of tiny house sales, where buyers often deal directly with builders or individual owners, requires diplomatic skills and emotional intelligence that differ from traditional real estate transactions [51]. Buyers who approach negotiations with aggressive tactics, unreasonable demands, or disrespectful attitudes often find that sellers become uncooperative or withdraw from discussions entirely, eliminating opportunities for successful deals.
Advanced Pro Tips for Seasoned Negotiators
Advanced psychological and strategic negotiation techniques for tiny house purchases
Master-level tiny house negotiation requires sophisticated psychological understanding and strategic thinking that goes beyond basic price discussions to create value for both parties while securing optimal outcomes. Professional negotiators recognize that the most successful tiny house transactions result from collaborative problem-solving approaches that address underlying needs and concerns rather than simply competing over price points [52]. These advanced techniques require practice and emotional intelligence but can result in significantly better deals and more satisfying outcomes for all parties involved.
Psychological anchoring techniques play a crucial role in establishing favorable negotiation frameworks, as the initial price discussions often set the boundaries for all subsequent negotiations. Experienced negotiators understand that the first number mentioned in any negotiation tends to anchor all following discussions around that reference point, making strategic use of this cognitive bias essential for optimal outcomes [53]. Rather than simply responding to seller asking prices, sophisticated buyers introduce their own anchoring points through detailed market analysis, comparable sales data, and objective valuation methodologies that shift the negotiation framework toward more favorable territory.
The strategic use of silence and pacing can dramatically improve negotiation outcomes by creating psychological pressure that encourages sellers to make concessions or reveal additional information. Many amateur negotiators feel compelled to fill conversational gaps with additional offers or explanations, inadvertently weakening their positions by appearing desperate or uncertain [54]. Professional negotiators use strategic pauses after making offers or hearing counteroffers, allowing the psychological weight of silence to encourage the other party to make the next move or provide additional concessions.
Building genuine rapport and personal connections with sellers creates negotiation advantages that extend far beyond simple price discussions, as people naturally prefer to do business with individuals they like and trust. The tiny house community’s emphasis on values, lifestyle, and personal relationships provides numerous opportunities for connection-building that can translate into more favorable negotiation outcomes [55]. Successful negotiators invest time in understanding sellers’ motivations, personal stories, and future plans, using this knowledge to structure deals that address emotional needs as well as financial objectives.
Creating win-win scenarios requires sophisticated understanding of both parties’ underlying needs and constraints, enabling creative solutions that provide mutual benefits while achieving individual objectives. Rather than viewing negotiations as zero-sum competitions where one party’s gain requires the other’s loss, advanced negotiators seek opportunities to expand the overall value of transactions through creative deal structures [56]. This might involve flexible closing timelines that accommodate sellers’ relocation needs, maintenance agreements that provide ongoing income opportunities, or referral arrangements that benefit builders’ future business development.
The strategic use of market data and third-party validation can significantly strengthen negotiation positions by providing objective support for price positions and terms requests. Rather than simply stating personal preferences or making unsupported demands, sophisticated negotiators present comprehensive market analysis, professional inspection reports, and expert opinions that justify their positions [57]. This approach transforms potentially adversarial price discussions into collaborative problem-solving sessions where both parties work together to address objective market realities.
Leveraging unique tiny house features and customization opportunities can create additional negotiation value that extends beyond simple price reductions. Many tiny house sellers have invested significant time and emotional energy in custom features, storage solutions, or design elements that may not appeal to all buyers but could provide significant value to the right purchaser [58]. Advanced negotiators identify these unique features and either negotiate for their inclusion at favorable prices or use their specialized appeal as justification for overall price adjustments.
The timing of concessions and offers requires strategic thinking about psychological impact and negotiation momentum, as the sequence and pacing of proposals can significantly influence final outcomes. Experienced negotiators understand that early concessions may be viewed as signs of weakness while late concessions can appear grudging or insufficient [59]. The most effective approach often involves graduated concession strategies that demonstrate good faith while maintaining negotiation leverage throughout the process.
Understanding and addressing seller psychology becomes particularly important in tiny house negotiations, where personal attachment, lifestyle values, and emotional investment often influence decision-making more than pure financial considerations. Many tiny house sellers have invested years of planning, significant personal labor, and emotional energy in their properties, creating psychological dynamics that differ dramatically from traditional real estate transactions [60]. Successful negotiators acknowledge these emotional investments while gently redirecting discussions toward objective market realities and mutual benefits.
Advanced contract negotiation techniques can create significant additional value through creative terms, conditions, and contingencies that protect buyer interests while addressing seller concerns. Rather than simply accepting standard contract terms, sophisticated negotiators propose customized provisions that address tiny house-specific issues such as ongoing compliance requirements, maintenance responsibilities, and potential relocation needs [61]. These advanced contract provisions often provide more long-term value than simple price reductions while demonstrating professional competence that encourages seller cooperation.
The strategic use of multiple negotiation channels and communication methods can provide advantages in complex transactions where different issues may be better addressed through various approaches. While face-to-face negotiations often work best for relationship building and major decisions, email communications can be effective for detailed technical discussions, while phone conversations may be optimal for time-sensitive issues [62]. Advanced negotiators match their communication methods to specific negotiation objectives while maintaining consistent messages across all channels.
Post-Negotiation Steps and Closing Process
The successful completion of tiny house negotiations marks the beginning of a critical transition period that requires careful attention to contract finalization, inspection processes, and closing preparations that differ significantly from traditional real estate transactions. Unlike conventional home purchases where established systems and professional oversight guide the closing process, tiny house transactions often require custom procedures and specialized attention to unique issues such as title transfer, registration updates, and compliance verification [63]. Understanding these post-negotiation requirements enables buyers to protect their investments while ensuring smooth transitions to ownership.
Contract finalization requires comprehensive review of all negotiated terms and conditions, with particular attention to tiny house-specific provisions that may not be covered in standard purchase agreements. The complexity of these transactions often necessitates custom contract language addressing issues such as trailer condition warranties, weight certifications, compliance with transportation regulations, and ongoing maintenance responsibilities [64]. Buyers should insist on detailed written documentation of all negotiated terms, including verbal agreements or understandings that might otherwise be forgotten or disputed during the closing process.
Final inspection procedures take on heightened importance in tiny house transactions due to the specialized systems and construction techniques that require expert evaluation. Unlike traditional home inspections that follow standardized procedures, tiny house inspections must address unique concerns such as weight distribution, electrical system capacity, plumbing functionality in mobile applications, and structural integrity under transportation stresses [65]. Professional inspectors with tiny house experience can identify potential problems that might not be apparent to general home inspectors, providing crucial protection against expensive post-purchase surprises.
The closing process itself often requires creative approaches to title transfer, registration updates, and financial transactions that accommodate the unique legal status of tiny houses. Depending on the property’s classification and local regulations, closing procedures might resemble vehicle sales, real estate transactions, or hybrid approaches that combine elements of both [66]. Buyers should work with experienced professionals who understand these complexities and can ensure that all legal requirements are met while protecting their interests throughout the transfer process.
Once you’ve successfully negotiated and purchased your tiny house, you’ll want to focus on making tiny house living rooms comfortable and exploring creative ways to maximize your space. Many new owners also find value in understanding 8 tiny house concepts with great loft spaces to optimize their vertical living arrangements.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of negotiating tiny house purchase like a pro requires a sophisticated understanding of market dynamics, legal complexities, and psychological principles that extend far beyond traditional real estate transactions. The unique challenges and opportunities presented by the tiny house market demand specialized knowledge, careful preparation, and strategic thinking that can mean the difference between securing an excellent deal and making costly mistakes that undermine your investment goals.
The strategies and techniques outlined in this comprehensive guide provide the foundation for successful tiny house negotiations, from understanding market trends and conducting thorough research to implementing advanced psychological tactics and managing complex closing processes. However, the most important element of successful negotiation remains the ability to maintain perspective, stay focused on your objectives, and walk away from deals that don’t meet your needs or budget constraints.
As the tiny house market continues to evolve and mature, buyers who master these negotiation principles will find themselves well-positioned to secure the best possible deals while avoiding the pitfalls that trap less-prepared purchasers. Whether you’re seeking your first tiny house or adding to an existing portfolio, these proven strategies will help you navigate the complexities of this unique market with confidence and success.
Remember that successful tiny house ownership extends beyond the purchase process, requiring ongoing attention to maintenance, compliance, and optimization of your living space. Consider exploring our comprehensive guides on tiny house floor plans and extending your tiny house to maximize comfort to ensure your investment provides years of satisfaction and value.
The tiny house movement represents more than just an alternative housing option—it’s a pathway to financial freedom, environmental responsibility, and intentional living that can transform your relationship with both money and space. By applying the negotiation strategies outlined in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to secure the tiny house of your dreams while protecting your financial interests and building the foundation for a more sustainable and fulfilling lifestyle.
References
[1] Tiny Homes Market to Grow by USD 3.71 Billion (2025-2029). Yahoo Finance. https://finance.yahoo.com/news/tiny-homes-market-grow-usd-055700574.html
[2] Are Tiny Homes Still Worth It in 2025? MoneyFit. https://www.moneyfit.org/tiny-homes/
[3] Are Tiny Homes A Good Investment? Reerin. https://reerin.com/are-tiny-homes-a-good-investment
[4] The Complete Guide to Tiny House Floor Plans. Tiny House Comfort. https://tinyhousecomfort.com/tiny-house-floor-plans-guide/
[5] Tiny Homes Market Growth Analysis – Technavio. https://www.technavio.com/report/tiny-homes-market-industry-services-analysis
[6] How Much Does a Tiny House Cost? Tiny Society. https://www.tinysociety.co/articles/how-much-money-does-a-tiny-house-cost/
[7] Tiny House Vacation Rentals: The Pros and Cons. Hostfully. https://www.hostfully.com/blog/tiny-house-vacation-rentals-benefits/
[8] Tiny House Laws by State. Tiny House Comfort. https://tinyhousecomfort.com/tiny-house-laws-by-state-guide/
[9] Navigating The Tiny House Market. Living in a Tiny. https://livinginatiny.com/navigating-the-tiny-house-market-a-comprehensive-guide/
[10] Tiny Homes in America: Latest Data. IPX1031. https://www.ipx1031.com/tiny-homes-in-america/
[11] 2025 Tiny Home Builder Trends. Nomadic Structures. https://www.nomadicstructuresinc.com/tiny-home-guide/tiny-home-builder-trends-for-2025-insights-from-the-industry
[12] Buying a used tiny house? Ask these 9 questions. The Tiny House. https://thetinyhouse.net/tiny-house-hunting-buying-a-used-tiny-house/
[13] 4 Steps to a Successful Tiny House Selling Journey. Off The MRKT. https://www.offthemrkt.com/lifestyle/4-steps-to-a-successful-tiny-house-selling-journey
[14] How to finance a tiny home. Yahoo Finance. https://finance.yahoo.com/personal-finance/mortgages/article/tiny-home-financing-193134694.html
[15] 6 Tips for Purchasing a Used Tiny Home on Wheels. Milgrom Law. https://www.milgromlaw.com/homebuying/6-tips-for-purchasing-a-used-tiny-home-on-wheels/
[16] Top Tips for Buying Land for Your Tiny Home. Tiny Society. https://www.tinysociety.co/articles/tips-for-buying-land-for-your-tiny-house/
[17] 5 Critical Things I Wish I Knew Before Buying a Tiny House. Tiffany the Tiny Home. https://www.tiffanythetinyhome.com/blog/2019/29/3-critical-things-i-wish-i-knew-before-buying-a-tiny-house
[18] How Much Does a Tiny House Cost? HomeGuide. https://homeguide.com/costs/tiny-house-cost
[19] Real Estate Negotiation Strategies. The Close. https://theclose.com/real-estate-negotiation/
[20] Message for all tiny home BUYERS. Facebook. https://www.facebook.com/tinyhouseconcierge/videos/message-for-all-tiny-home-buyers-its-time-to-negotiate-a-bitwant-to-know-how-to-/1809928769501774/
[21] Watch This Before Buying or Building A Tiny House! YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XxY-cEyLB7Y
[22] 5 Home Negotiation Strategies. Truist Bank. https://www.truist.com/resources/mortgage/articles/5-home-negotiation-strategies
[23] Things I Wish I Knew Before Buying a Tiny House. Buy a Small House. https://buyasmallhouse.com/things-i-wish-i-knew-before-buying-a-tiny-house/
[24] Tiny House Purchase Guide. Team Vasquez. https://teamvasquez.house/guides/tiny-house-purchasing-simplified-process-and-tips/
[25] Unlocking Freedom by Financing Tiny House. DA’TINY Homes. https://dtinyhomes.com/financing-tiny-house/
[26] How much is a tiny house? Rocket Mortgage. https://www.rocketmortgage.com/learn/how-much-does-a-tiny-house-cost
[27] How Much Does a Tiny House Cost? Home Gnome. https://homegnome.com/blog/cost/tiny-house-price/
[28] Tiny House Costs: The Pros and Cons. TenantCloud. https://www.tenantcloud.com/blog/tiny-house-costs-the-pros-and-cons-of-living-minimally
[29] Selling Your Tiny Home on Wheels? Tiny House Society. https://tinyhousesociety.com/selling-your-tiny-home-on-wheels-heres-how-to-price-it-right/
[30] How Much Does a Tiny House Really Cost? The Spruce. https://www.thespruce.com/tiny-house-cost-8604331
[31] How to Negotiate House Price For Buyers. Quicken Loans. https://www.quickenloans.com/learn/how-to-negotiate-house-price
[32] The 8 Steps To Buying A Tiny House. BB Tiny Houses. https://bbtinyhouses.com/how-to-buy-a-tiny-house-everything-youll-need-to-know/
[33] Are Tiny Homes Worth It? 21 Reasons Why They’re a Huge Mistake. Yahoo Finance. https://finance.yahoo.com/news/tiny-homes-worth-21-reasons-100400803.html
[34] What You Need To Know Before Buying a Tiny House. LowerMyBills. https://www.lowermybills.com/learn/buying-a-home/buying-tiny-home/
[35] Tiny House Reality Check! YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IV5rv8AYUsk
[36] Tiny House Tips: 14 Things to Consider Before Building. Hachette Book Group. https://www.hachettebookgroup.com/storey/tiny-house-tips-14-things-consider-before-building/
[37] The Big Guide to Tiny House Living. Family Handyman. https://www.familyhandyman.com/article/guide-to-tiny-house-living/
[38] Small House Movement. National Association of REALTORS. https://www.nar.realtor/small-house-movement
[39] Tiny homes: What you need to know before you buy one. USA Today. https://www.usatoday.com/story/money/personalfinance/real-estate/2022/06/28/tiny-homes-mortgages-depreciation-insurance/50419377/
[40] Tiny Home Buying Guide. Piccola Tiny Homes. https://piccolatinyhomes.com/tiny-home-buying-guide-your-essential-steps-to-success/
[41] How to Buy Your First Tiny Home. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gM3Pa3SBV5M
[42] 8 Things I Wish I Knew Before Buying a Tiny Home. Apartment Therapy. https://www.apartmenttherapy.com/tiny-house-living-experience-260709
[43] Why a Tiny House Might Not Be As Affordable As You Think. Lifehacker. https://lifehacker.com/why-a-tiny-house-might-not-be-as-affordable-as-you-thin-1849847134
[44] 7 Things You Should Never Do When You’re Negotiating. Apartment Therapy. https://www.apartmenttherapy.com/how-to-negotiate-house-price-mistakes-265381
[45] “Where do I start?” How to buy a tiny house. Trailhead Tiny. https://trailheadtiny.com/how-to-buy-a-tiny-house/
[46] First Tiny Home Advice? Reddit. https://www.reddit.com/r/TinyHouses/comments/sxbo7m/first_tiny_home_advice/
[47] How Much Tiny Houses Really Cost? Autonomous. https://www.autonomous.ai/ourblog/how-much-tiny-homes-really-cost
[48] How to Start Living in a Tiny Home. Dumpsters.com. https://www.dumpsters.com/blog/living-in-a-tiny-house
[49] 5 Negotiation Strategies For Home Buyers. Roongta Developers. https://www.roongtadevelopers.com/blog-detail/5-proven-negotiation-strategies-for-home-buyers-try-now
[50] Real Estate Negotiation Strategies. RentSpree. https://www.rentspree.com/blog/real-estate-negotiation
[51] 8 Real Estate Negotiation Strategies. Leelana Realtors. https://leelanaurealtors.com/blog/8-real-estate-negotiation-strategies-from-an-expert
[52] Negotiation Examples in Real Life. Harvard PON. https://www.pon.harvard.edu/daily/business-negotiations/dealing-with-an-irrational-home-seller/
[53] Real Estate Negotiation Strategies. The Bar Group. https://thebargroup.com/blog/real-estate-negotiation-strategies-from-an-expert
[54] Mastering the Art of Real Estate Negotiation. Luxury Presence. https://www.luxurypresence.com/blogs/real-estate-negotiation-strategies/
[55] Real estate negotiation: 8 effective strategies. Housing Wire. https://www.housingwire.com/articles/real-estate-negotiation/
[56] 8 Real Estate Negotiation Strategies & Tips. SignMore. https://www.signmore.com/know-more/real-estate-negotiation
[57] Negotiation Strategies for Sellers. Lux Life Miami Blog. https://luxlifemiamiblog.com/real-estate-negotiation-strategies-for-sellers-techniques-from-chris-vosss-playbook/
[58] Here’s What You Can (And Can’t) Negotiate. HomeLight. https://www.homelight.com/blog/buyer-buying-new-construction-home-negotiation/
[59] Negotiation Tips and Tricks Your Home Builder Won’t Talk About. Construct Elements. https://www.constructelements.com/post/negotiation-tips-and-tricks-your-home-builder-wont-talk-much-about
[60] Is Buying a Tiny House an Affordable Alternative to Renting? Experian. https://www.experian.com/blogs/ask-experian/buying-tiny-house-vs-renting/
[61] Expert Tips to Find and Buy Land For Your Tiny House. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HIhwX0ZMgbQ
[62] 7 INSANE Negotiation Tactics for Real Estate Agents. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TTNt-fB2ZYo
[63] Quick Guide: How To Sell Your Tiny House Fast. Tiny House Plans. https://www.tinyhouseplans.com/blogs/guides/how-to-sell-your-tiny-house-fast
[64] Should I buy a used tiny house? Stuff. https://www.stuff.co.nz/home-property/350400784/should-i-buy-used-tiny-house
[65] Tiny House Builder Shares Real Costs. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IM0h0xBSQ6Q
[66] How much does it cost to build a tiny house? Fixr.com.